An alloy is a material composed of two or more metallic elements, or a combination of metallic and non-metallic elements, fused together to create a new substance with distinct physical and chemical properties different from those of its constituent metals. Our company has the various alloy for sale, and the solution is customerized for you.
Alloy Rolling Process
The alloy rolling process is a metalworking technique used to shape and reduce the thickness of alloy materials, such as nickel-based alloys (e.g., Monel, Hastelloy), stainless steels, and other high-performance metals. This process involves passing the alloy through a pair of rotating rolls under high pressure to achieve the desired thickness, shape, and mechanical properties. Rolling is a critical step in the production of sheets, strips, plates, bars, and other forms of alloy products used in various industries. Huaxiao Metal Manufacturer is professional, as a distributer, we have the assurance about alloy products, I am convienced that you will ba satisfied with the alloy products and the service.


Alloy Rolling Process is benefit to the alloy and let the alloy more strong. We have a large amount of high-quality alloy inventory ready for shipment, please request a quote immediately.
The Composition of Alloys
| Alloy Grade | Major Elements and Their Composition (%) |
|---|---|
| 6063 | Si: 0.2-0.6, Fe: 0.35, Cu: 0.1, Mn: 0.1, Mg: 0.45-0.9, Cr:<0.1, Zn:<0.1, Ti:<0.1, Zr:<0.05, Other:<0.15, Residual Aluminum: Balance |
| 6061 | Si: 0.4-0.8, Fe: 0.7, Cu: 0.15-0.4, Mn: 0.15, Mg: 0.8-1.2, Cr: 0.04-0.35, Ni:<0.1, Zn:<0.25, Ti:<0.15, Zr:<0.05, Other:<0.15, Residual Aluminum: Balance |
| 6005 | Si: 0.6-0.9, Fe: 0.35, Cu: 0.1, Mn: 0.1, Mg: 0.4-0.6, Cr:<0.1, Zn:<0.1, Ti:<0.1, Zr:<0.05, Other:<0.15, Residual Aluminum: Balance |
| 5A02 | Al-Mg alloy with significant Mg content, specific composition may vary |
| 5A05 | Al-Mg alloy with Mg as the primary alloying element, specific composition may vary |
| 2A12 | Cu: 3.8-4.9, Mg: 1.2-1.8, Mn: 0.3-0.9, Fe:<0.5, Si:<0.5, Zn:<0.3, Cr:<0.1, Ti:<0.15, Other:<0.15, Residual Aluminum: Balance |
The Properties of Alloys
Physical Properties of Alloy
| Alloy Type | Density (g/cm³) | Elastic Modulus (GPa) | Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) | Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (10^-6/°C) | Melting Point (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloy 6061 | 2.7 | 70-80 | 160-200 | 23.6 | 600-660 |
| Brass (Cu-Zn Alloy) | 8.4-8.7 | 100-130 | 109-121 | 17.5 | 890-950 |
| Bronze (Cu-Sn Alloy) | 8.5-8.8 | 110-130 | 70-100 | 17-19 | 800-950 |
| Stainless Steel 304 | 7.93 | 190-210 | 14-30 | 17.3 | 1400-1450 |
| Nickel-Chromium Alloy (Inconel 600) | 8.44 | 200-220 | 12.5-16.5 | 13.3 | 1300-1370 |
| Titanium Alloy (Ti-6Al-4V) | 4.5 | 110-120 | 7-9 | 8.6 | 1600-1650 |
Alloy Rolling Process is a tip of strengthening the alloy properties. Our company have a large amount of high-quality alloy inventory ready for shipment, please request a quote immediately.
Mechanical Properties of Alloy
| Alloy Type | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) | Hardness (HB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloy 6061-T6 | 276-311 | 241 | 12-20 | 60-70 |
| Brass (Cu-30%Zn) | 340-470 | 200-300 | 10-35 | 80-120 |
| Bronze (Cu-10%Sn) | 300-400 | 150-250 | 5-20 | 70-110 |
| Stainless Steel 304 | 500-700 | 205 | 30-40 | 187 |
| Nickel-Chromium Alloy (Inconel 600) | 620-820 | 240-415 | 30-40 | – |
| Titanium Alloy (Ti-6Al-4V) | 890-980 | 790-860 | 10-15 | 310-360 |
The alloy can be better by using of the Alloy Rolling Process. We have a large amount of high-quality alloy inventory ready for shipment, please request a quote immediately.
Features of Rolling Process
Alloy Rolling Process has many of advantages, Huaxiao Metal Supplier has some examples about alloy rolling process:
Strength and Hardness: Alloy often exhibit higher strength and hardness compared to their constituent pure metals. This is due to the solid solution strengthening, precipitation hardening, and grain refinement effects that occur when alloying elements are added.
Corrosion Resistance: Many alloy, such as stainless steels and nickel-based alloys, are designed to resist corrosion in specific environments. The addition of chromium, nickel, molybdenum, and other elements can significantly enhance corrosion resistance.
Thermal Conductivity and Electrical Conductivity: The thermal and electrical conductivity of alloy can vary depending on their composition. Some alloys, such as copper-based alloys, are known for their high electrical conductivity, while others, like aluminum alloys, have good thermal conductivity.
Ductility and Toughness: Alloys can exhibit a range of ductility and toughness. Ductile alloy can undergo significant plastic deformation without fracturing, while tough alloy can absorb a large amount of energy before failing. The balance between these properties depends on the alloy composition and processing methods.



Alloy Rolling Process is a method of improve the alloy properties. We have a large amount of high-quality alloy inventory ready for shipment, please request a quote immediately. Our service is customerized for erery customer and the produce is public and fast about alloy products in line.
Key Steps in the Alloy Rolling Process
In essence, rolling processes are the cornerstone of modern metalworking. They facilitate the transformation of raw materials into the countless products that are essential our daily lives. Through the meticulous coordination of force and temperature, this process can precisely and efficiently produce everything from sheets to complex profiles. Understanding the behind rolling can illuminate its immense industrial significance and pave the way for the continued advancement of metal forming technologies. As we delve deeper into the complexities of rolling, we innovative new possibilities, ensuring its enduring relevance in the evolving landscape of manufacturing.
1. Heating (Optional):
Some alloys, especially those that are hard or brittle at room temperature, are heated to make them more malleable. This is known as hot rolling.
For softer alloys or those requiring precise dimensions, cold rolling is performed at room temperature.
2. Initial Rolling:
The alloy is passed through a set of rolls to reduce its thickness and shape it into a rough form, such as a slab or billet.
3. Intermediate Rolling:
The material undergoes further rolling to achieve intermediate dimensions and improve its mechanical properties.
4. Final Rolling:
The alloy is rolled to its final dimensions, ensuring precise thickness, surface finish, and mechanical properties.
5. Heat Treatment (Optional):
After rolling, some alloys undergo heat treatment (e.g., annealing, precipitation hardening) to enhance their strength, ductility, or corrosion resistance.
6. Surface Finishing:
The rolled alloy may undergo additional processes like polishing, pickling, or coating to improve its surface quality and performance.
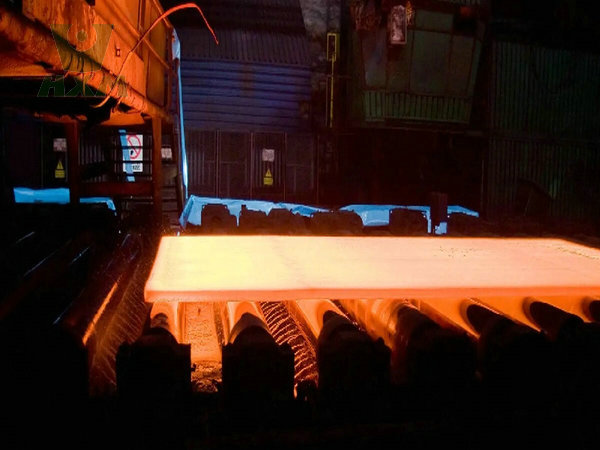



Types of Rolling Process
Hot Rolling:
Performed at temperatures above the alloy’s recrystallization point.
Advantages:
Reduces energy required for deformation.
Improves ductility and workability.
Applications: Producing thick plates, sheets, and structural components.
Cold Rolling:
Performed at room temperature.
Advantages:
Provides better surface finish and tighter dimensional tolerances.
Increases strength and hardness through work hardening.
Applications: Producing thin sheets, strips, and foils.
Warm Rolling:
Performed at intermediate temperatures (below recrystallization but above room temperature).
Advantages:
Balances the benefits of hot and cold rolling.
Applications: Used for specific alloys requiring precise mechanical properties.
Comparison of Hot Rolling vs. Cold Rolling
| Parameter | Hot Rolling | Cold Rolling |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Above recrystallization temperature | Room temperature |
| Surface Finish | Rough, scaled surface | Smooth, polished surface |
| Dimensional Accuracy | Less precise | Highly precise |
| Mechanical Properties | Improved ductility, lower strength | Increased strength, reduced ductility |
| Applications | Thick plates, structural components | Thin sheets, strips, foils |
How Are Rolling Process?
Alloy Rolling Process is made through the process of alloying, which involves combining two or more metallic elements, including at least one metal, in precise proportions. This can be achieved by either mixing molten metals or metal powders. The metals used in alloys can vary widely, such as copper, aluminum, iron, nickel, titanium, and many others.
Additionally, non-metals like carbon and silicon can also be incorporated into the alloy composition. The desired elements are melted or mixed together under controlled conditions to ensure the desired alloy composition and properties are achieved.Huaxiao Metal Supplier has the over 10 years in producing alloy, which our company have ourselves alloy factory and the quality is good and delivery is fast, welcome to inquiry and ask for some solutions about any alloy questions. Of course, our service is customerized for every customers from the different countries.
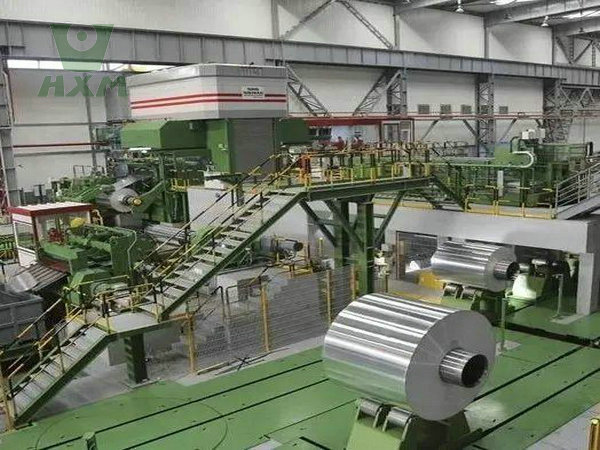
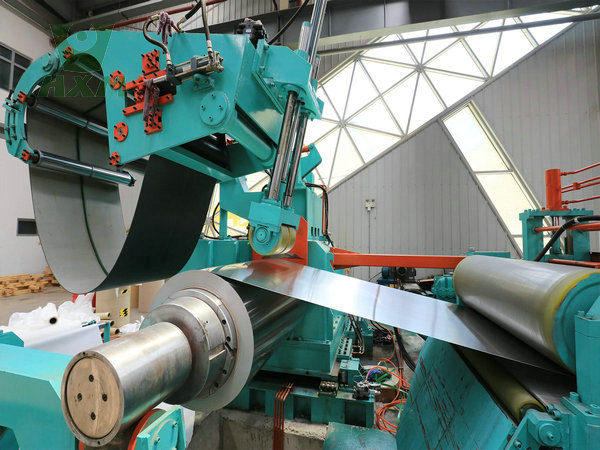



Other Benefits of Rolling Process Manufacturing
Improved Mechanical Properties:
Rolling enhances the strength, hardness, and ductility of alloys through work hardening and grain refinement.
Precision and Consistency:
The process allows for precise control over thickness, width, and surface finish, ensuring consistent quality.
Versatility:
Rolling can produce a wide range of products, including sheets, strips, plates, bars, and structural shapes.
Cost-Effectiveness:
High production rates and minimal material waste make rolling an economical manufacturing method.
Enhanced Corrosion Resistance:
Rolling can improve the microstructure of alloys, enhancing their resistance to corrosion and wear.
Industries that Rolling Process Applications
Aerospace:
Rolled sheets and strips are used in aircraft components, turbine blades, and structural parts.
Chemical Processing:
Corrosion-resistant alloys like Hastelloy are rolled into sheets and strips for reactors, heat exchangers, and piping.
Oil and Gas:
Rolled plates and bars are used in offshore platforms, pipelines, and downhole equipment.
Marine Engineering:
Rolled Monel and other nickel-based alloys are used in seawater valves, pump shafts, and propeller shafts.
Electronics:
Thin strips and foils are used in electronic components, connectors, and battery materials.



In Conclusion
The alloy rolling process is a fundamental manufacturing technique that transforms raw alloy materials into high-quality products with precise dimensions and enhanced mechanical properties. Whether through hot rolling, cold rolling, or warm rolling, this process plays a crucial role in producing materials for industries such as aerospace, chemical processing, oil and gas, and electronics. By understanding the rolling process, manufacturers can optimize production, improve product performance, and meet the demanding requirements of modern applications.
Alloy Rolling Process Alloy works by combining the properties of their constituent metals in a way that creates a new material with unique and often superior characteristics. These characteristics can include high strength, corrosion resistance, high melting points, and tailored physical properties. By adjusting the composition and processing methods of the alloy, it can be tailored to meet specific application requirements.Alloy is created by combining different metallic and non-metallic elements in precise proportions. They work by leveraging the combined properties of these elements to create a new material with superior characteristics tailored to specific applications. Huaxiao Metal Supplier is for sale alloy product to customer.
In conclusion, the alloy rolling process is a fundamental technique in modern manufacturing. Its ability to shape and strengthen metal alloys makes it indispensable in the production of high-quality components for various industries. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovations and improvements in the alloy rolling process, driving the manufacturing industry towards greater efficiency and sustainability. By staying up-to-date with the latest trends and techniques, manufacturers can ensure that they remain competitive in the global market and continue to produce innovative, high-quality products that meet the demands of today’s consumers.
